Guide to Zoning Terms
Buffer
An area designed to separate properties with different purposes. For example, hedge rows or walls separating residential and commercial uses.
Landscaping
Carefully planned green space. In an urban environment, this would include street trees, gardens, flowerpots, and parks.
Pedestrian Infrastructure
Elements that create a positive and safe experience for those on foot, such as crosswalks, wide sidewalks, flower pots, lighting, separation from traffic and a low traffic speed.
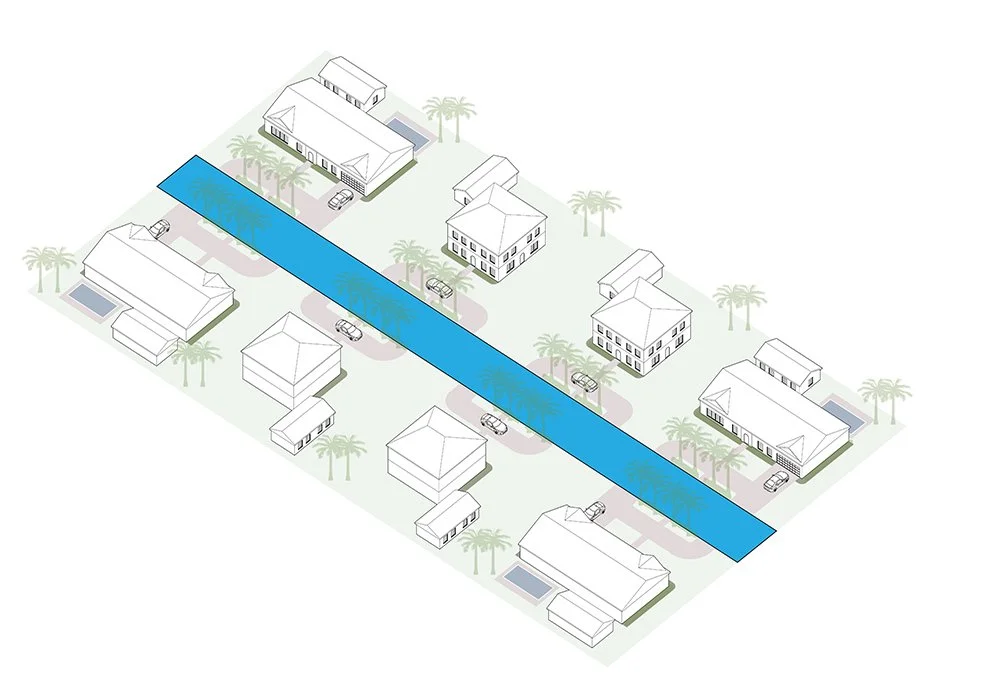
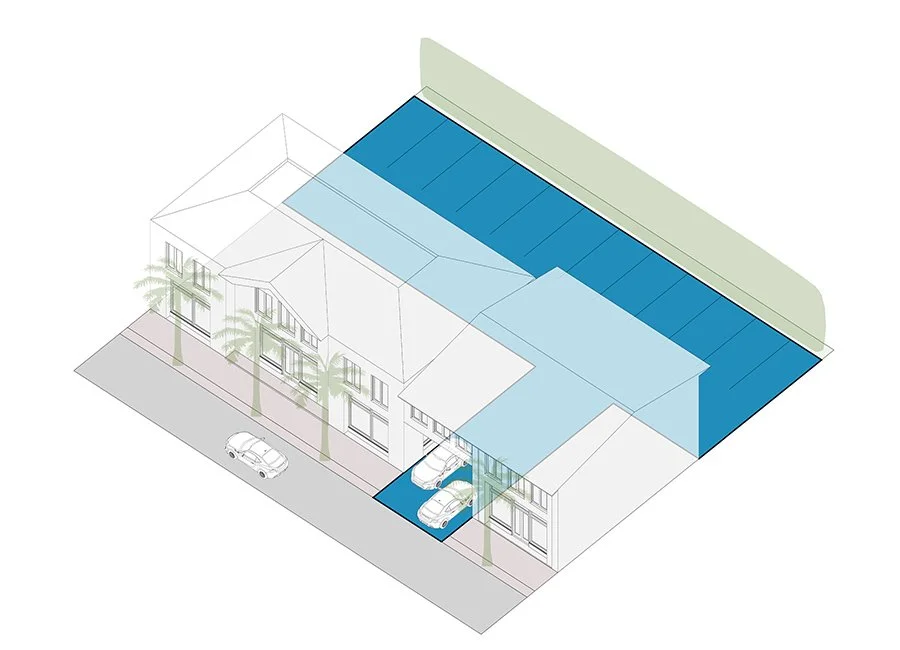
Right of Way
The strip of land that is used for a street or utility lines. In an urban environment, the right of way is typically owned by the municipality and includes sidewalks, planting strip buffers, curbs, streets, and medians. Alleys are also often part of the public right of way.
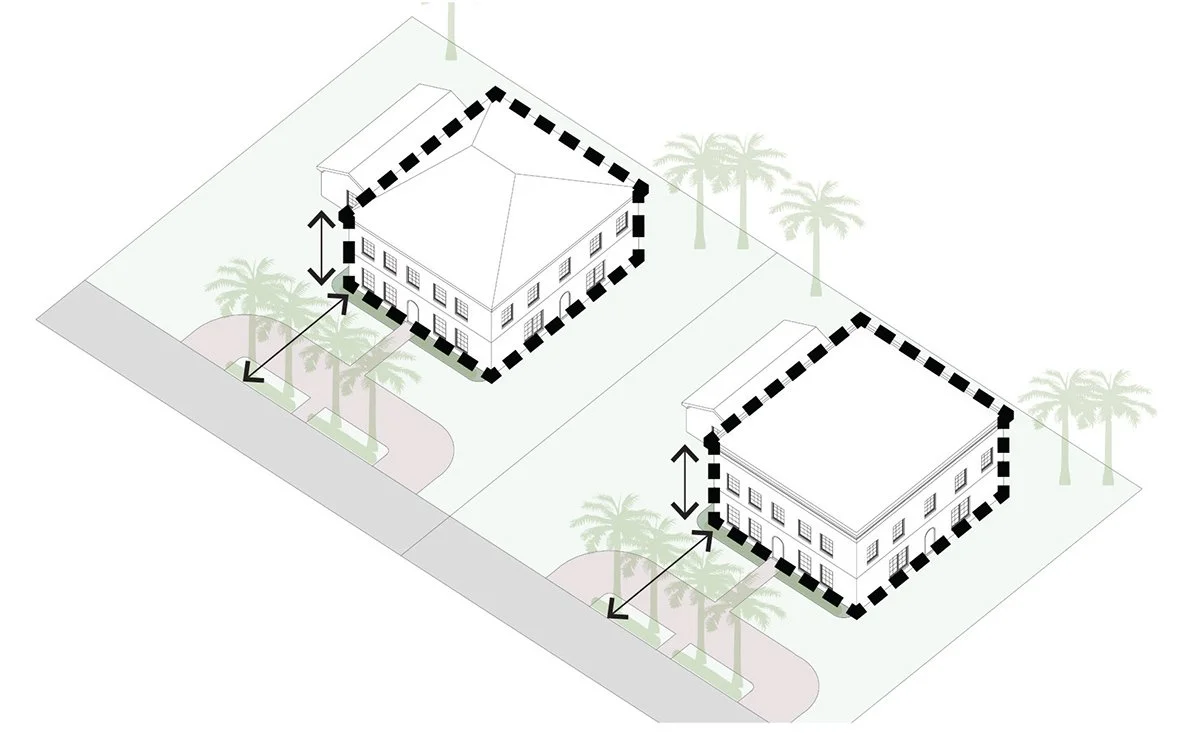
Scale
A building’s size in relation to other buildings around it and in comfortable proportion to the street/sidewalk.
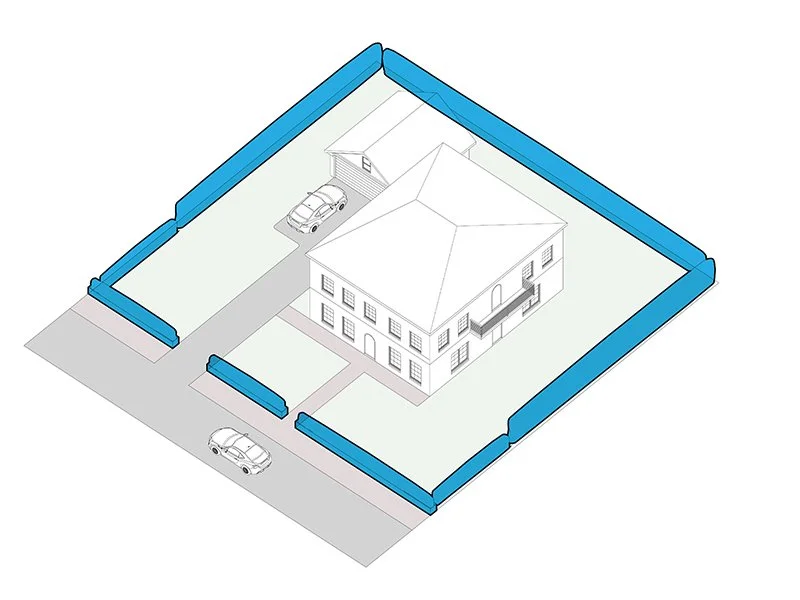
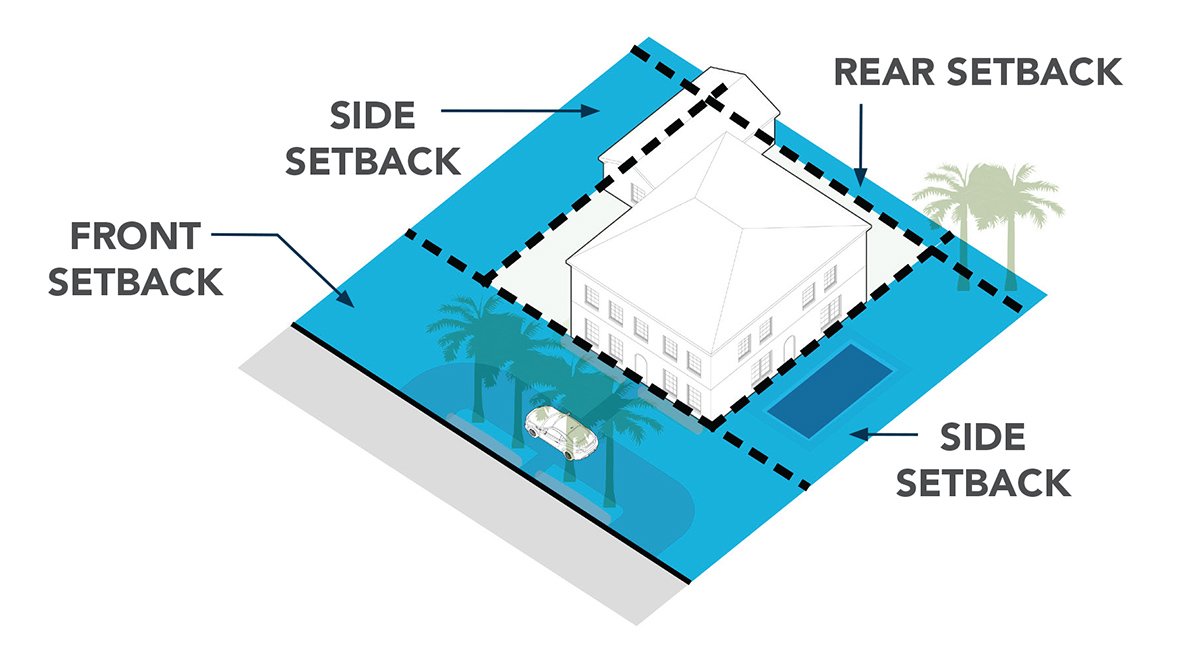
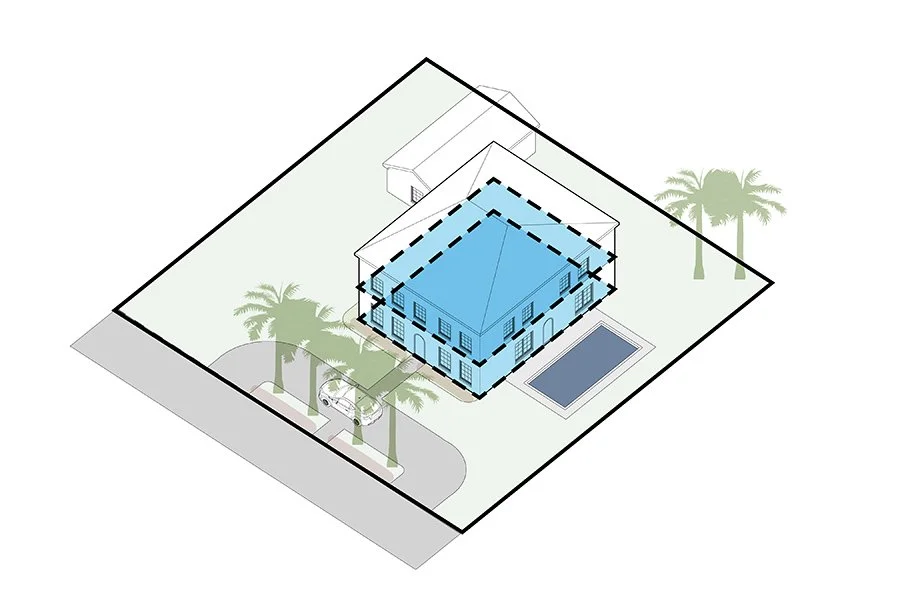
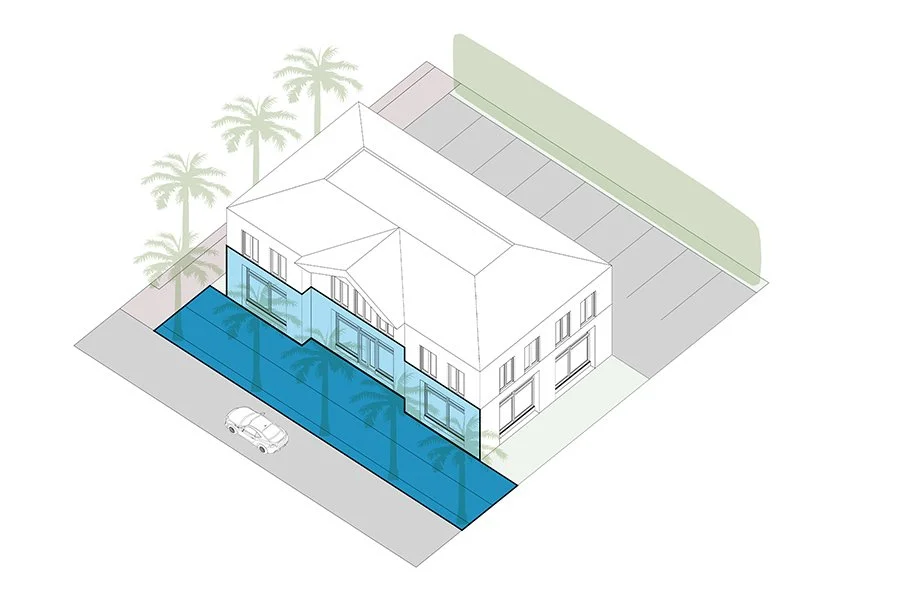
Setback
The distance between a building and the street, lot line and/or other buildings.
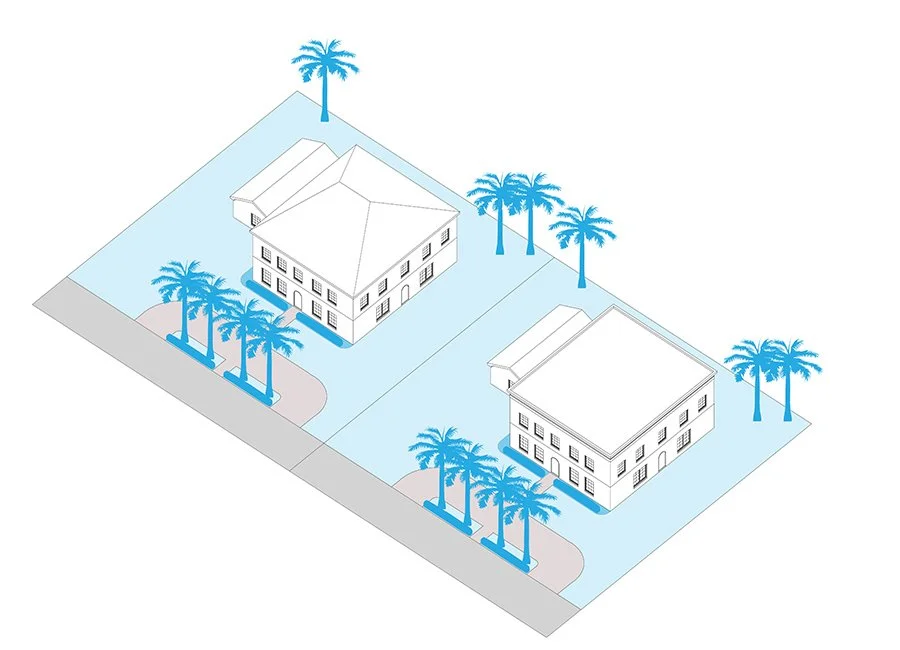
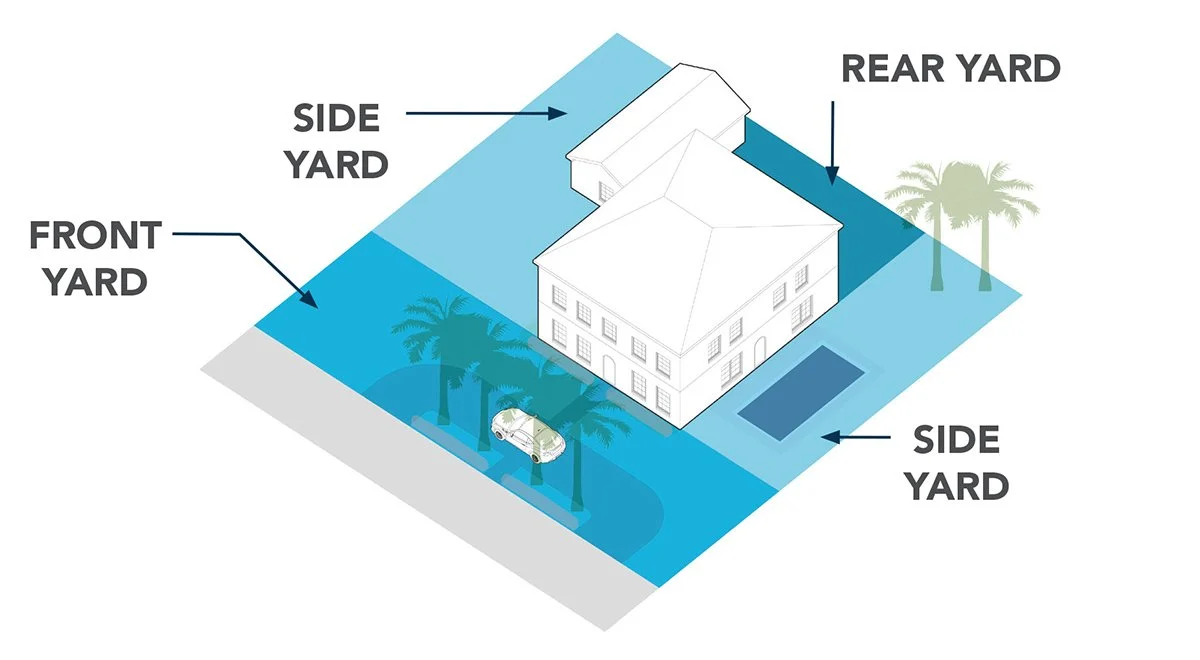
Yard
A property’s open space, i.e. the grounds immediately surrounding a building or, in the case of a courtyard, within a building.
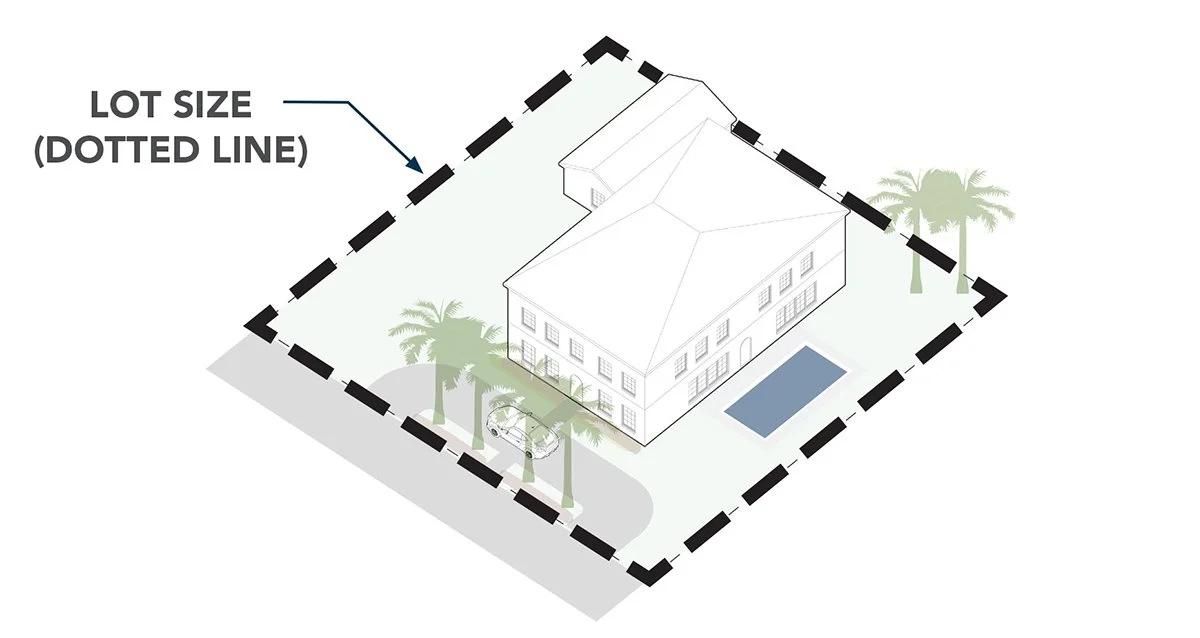
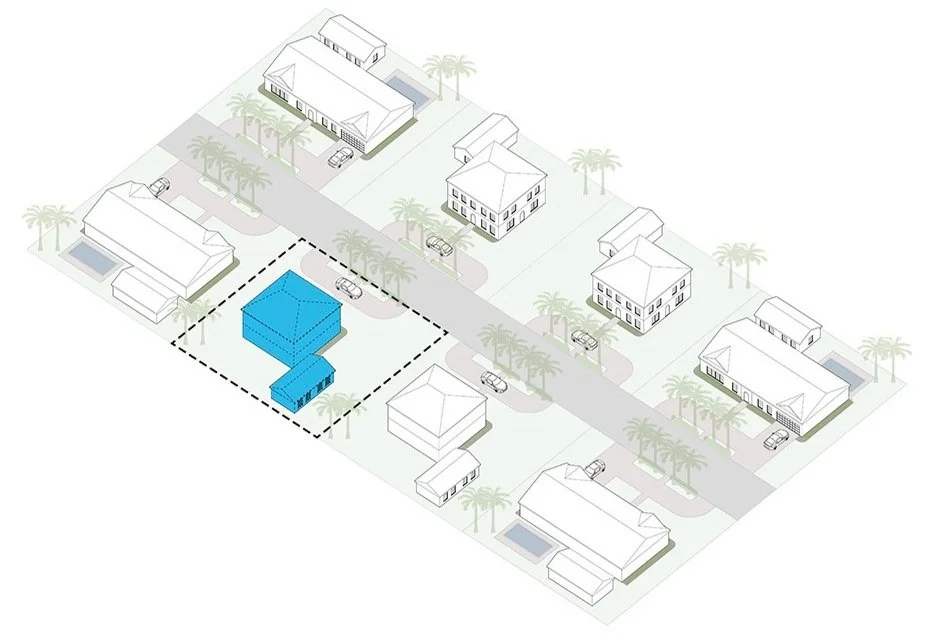
Lot Size
The total area of a property, typically measured in square feet or acres.
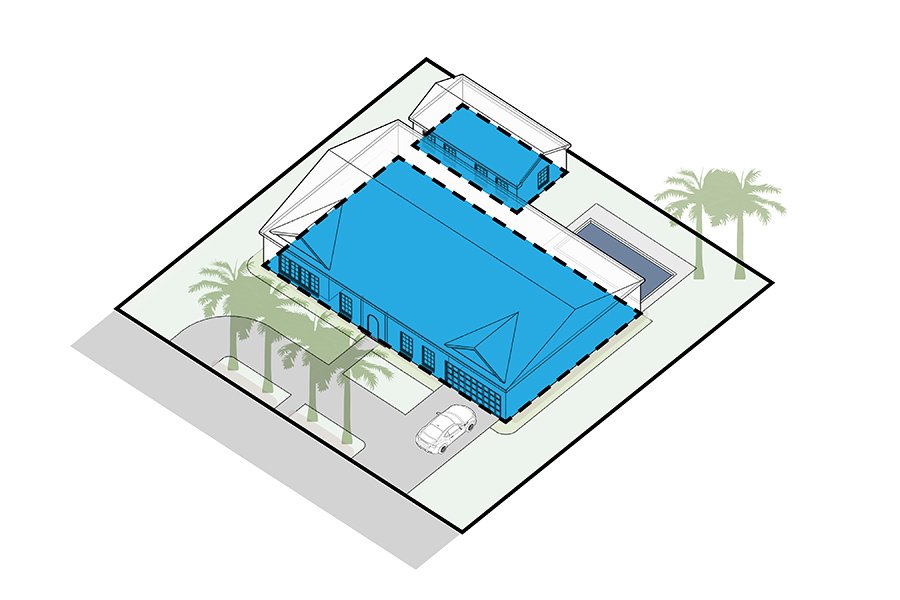
Lot Coverage Ratio
A number that depicts the relationship between the size of building(s) and the size of the lot they occupy.
Floor Area Ratio
A number that represents the floor area of a building in relation to the lot area it occupies.
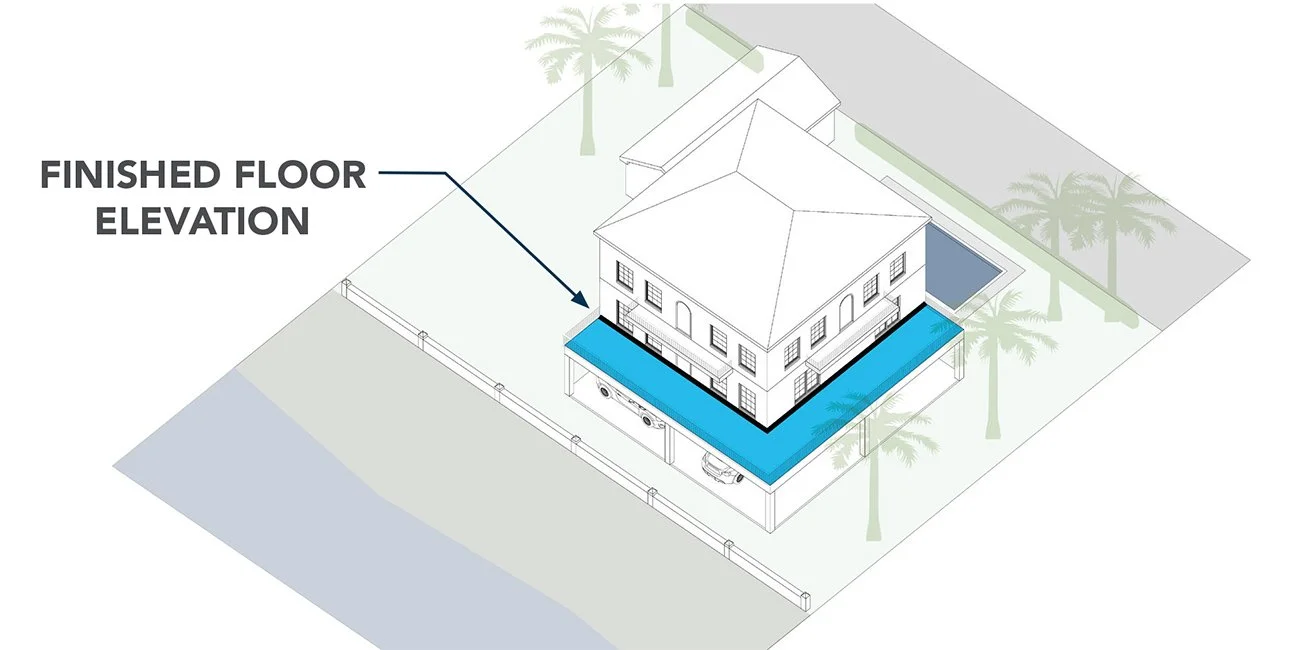
Finished Floor Elevation
The minimum height above sea level the firstfloor must be. This is important in areas that experience flooding or sea level rise.
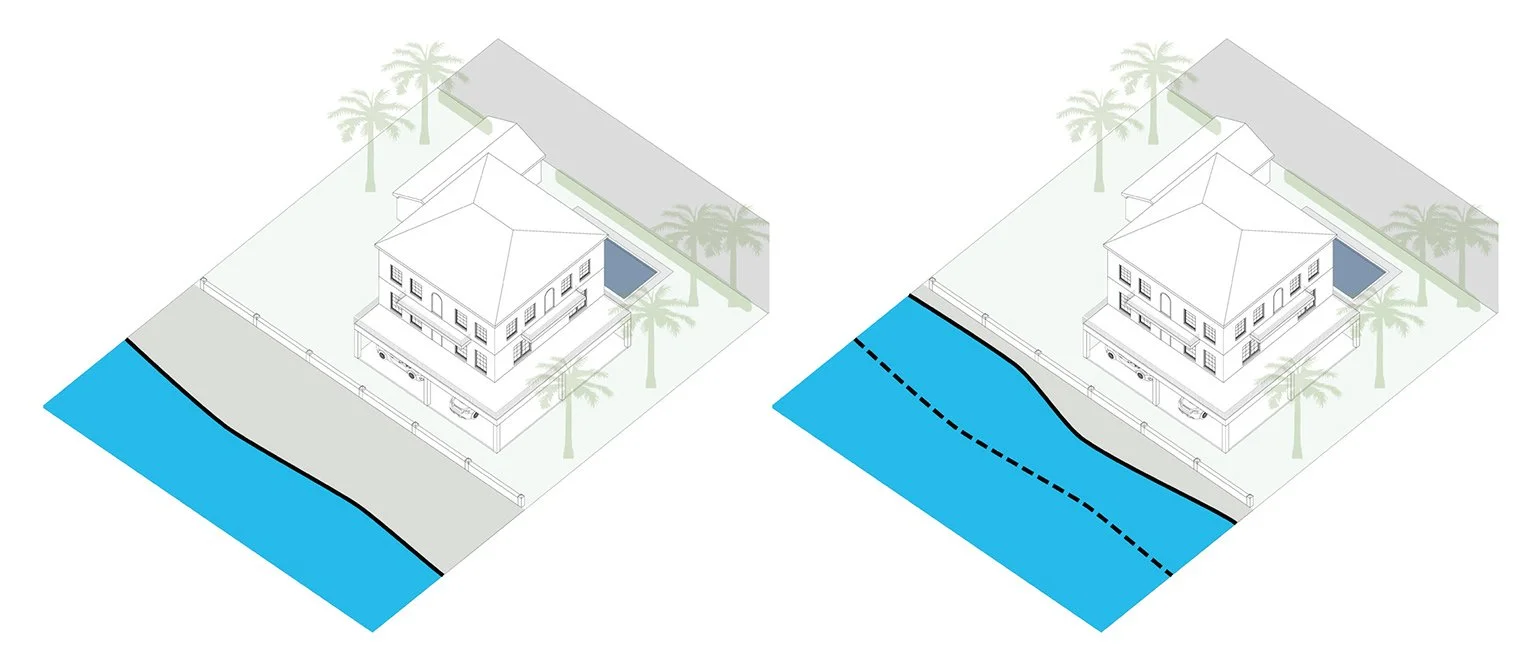
Sea Level Rise
The increase in the average reach of the ocean over land.
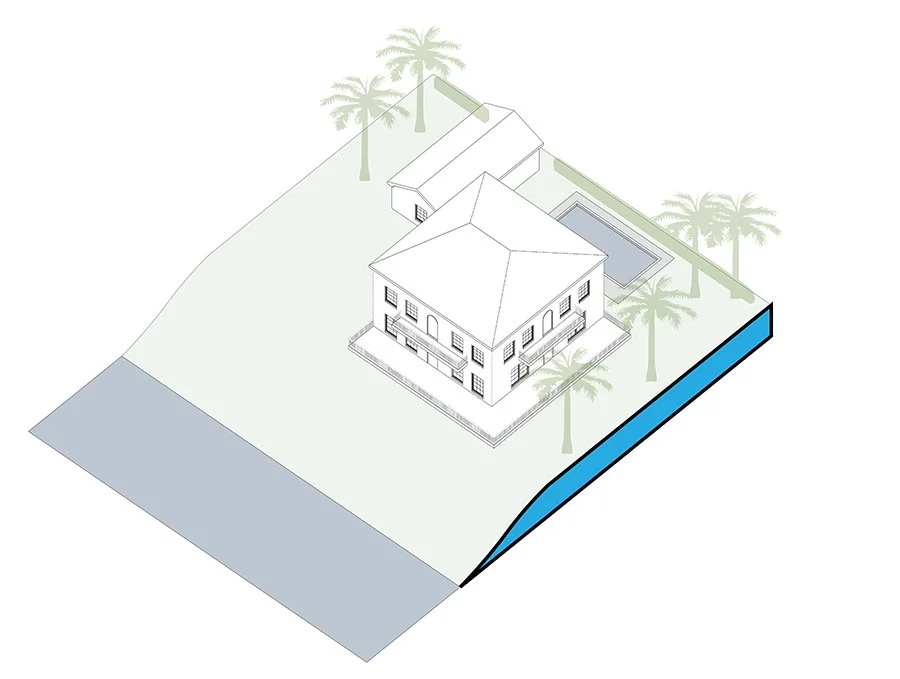
Fill
Soil and other materials imported to a building site to elevate the site higher than its current state.
Stepback
The way upper floors of a building step back from the street.
Frontage Zone
The part of the property where most or all of the front of a building must locate.
Infill
New building construction on a street with existing buildings.
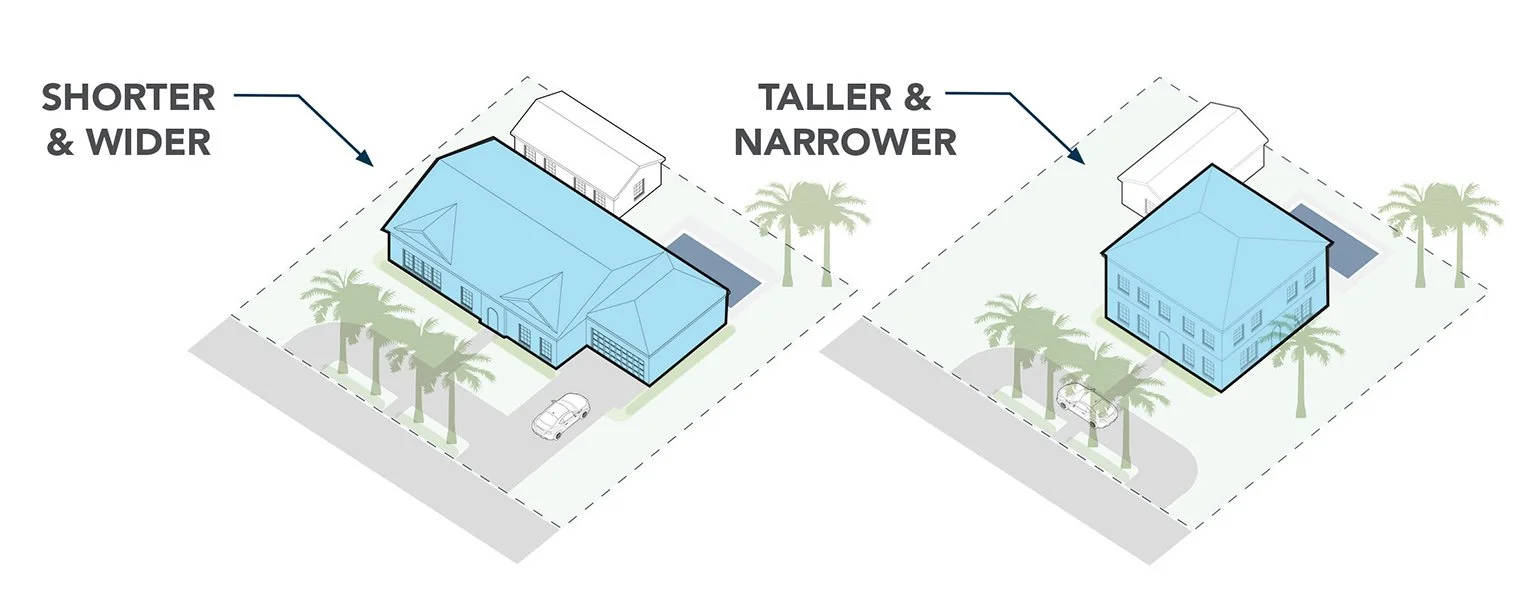
Massing
The way a building’s square footage is distributed on a lot. For example, is the building tall and skinny or short and wide?
Parking Minimum
The number of parking spaces required for a building relative to the type(s) of uses in the building.
Parking Ratio
A statistic used to determine how much parking a building must have. This is typically measured as spaces per 1,000 square feet of non-residential use or the number of spaces per residential unit or bedroom.
Transparency
The proportion of openings such as windows and doors to walls.